
For example, the neutron number of uranium-238 is 238-92=146. We can determine the neutron number of certain isotope.
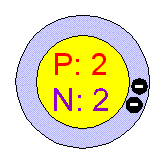
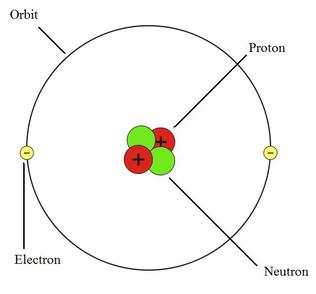
Therefore, we cannot determine the neutron number of uranium, for example. Each nuclide is denoted by chemical symbol of the element (this specifies Z) with tha atomic mass number as supescript. The various species of atoms whose nuclei contain particular numbers of protons and neutrons are called nuclides. Nuclides that have the same neutron number but a different proton number are called isotones. Neutron number is rarely written explicitly in nuclide symbol notation, but appears as a subscript to the right of the element symbol. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Helium are 3 4. See also: Atomic Mass Number – Does it conserve in a nuclear reaction? According to the Einstein relationship ( E=mc 2), this binding energy is proportional to this mass difference and it is known as the mass defect. The difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which holds the nucleus together. Mass was no longer considered unchangeable in the closed system. Note that, it was found the rest mass of an atomic nucleus is measurably smaller than the sum of the rest masses of its constituent protons, neutrons and electrons. For 63Cu the atomic mass is less than 63 so this must be the dominant factor. A nucleus with greater binding energy has a lower total energy, and therefore a lower mass according to Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence relation E = mc 2. The nuclear binding energy varies between nuclei.This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit scale based on 12C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons.
The fact that para-helium energy levels lie slightly above corresponding ortho-helium levels is interesting because our original Hamiltonian does notĭepend on spin. As we have seen, for the ground state, only para-helium is possible. Incidentally, helium in the spin singlet state is known as para-helium, whereas helium in the triplet state isĬalled ortho-helium. Hence, we conclude that in excited states of helium the spin singlet state has a higher energy which is known as the exchange integral-canīe shown to also be positive. which is known as the direct integral-is obviously positive.
#Mass of helium atom plus#
Here, the plus sign in ( 1095) corresponds to the spin singlet state, whereas the minus sign corresponds to the spin triplet state.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
